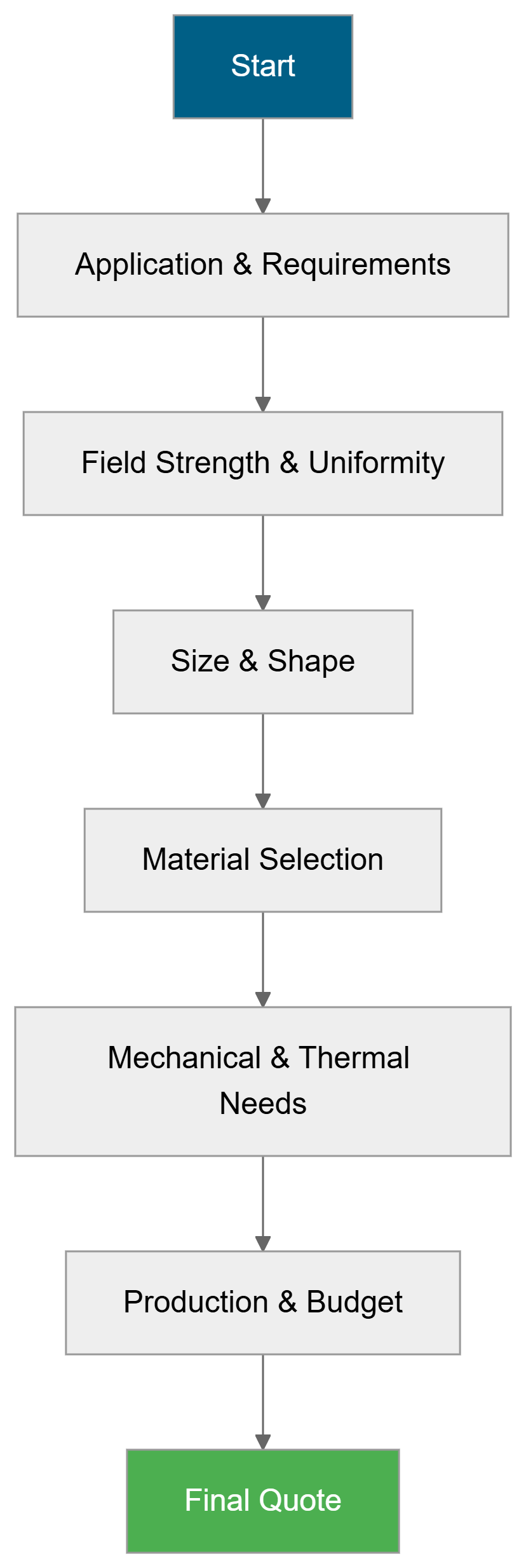
To provide accurate quotes and solutions for Halbach Array, we need to know the following key information:
1. Application scenarios and requirements
- Use: For motors, magnetic levitation, particle accelerators, sensors, medical equipment, etc.? Different scenarios have different performance requirements for magnets.
- Target function: Do you need to enhance magnetic field strength, uniformity, directional magnetic field, or other specific goals?
- Environmental conditions: Are high temperature, low temperature, vacuum, corrosive environment or radiation environment involved?
2. Magnetic performance parameters
- Magnetic field strength: Required surface magnetic field strength (such as Tesla or Gauss) and effective range.
- Magnetic field direction: The magnetic field direction of the Halbach array (radial, axial or other customized directions).
- Uniformity requirements: Does the magnetic field need to be highly uniform? What is the allowable fluctuation range?
- Operating temperature: In what temperature range does the magnet work? Is temperature stability compensation required?
3. Geometry and structural design
- Size and shape: The overall size (diameter, length, thickness, etc.) and shape (ring, flat, arc, etc.) of the magnet.
- Halbach array type: classic Halbach, segmented, hybrid? What is the number of pole pairs (number of magnetic poles)?
- Installation space constraints: Are there any space constraints or mechanical integration requirements (such as coordination with other components)?
4. Material selection
- Magnetic material: neodymium iron boron (NdFeB), samarium cobalt (SmCo), ferrite or other? Consider remanence, coercivity, temperature coefficient, etc.
- Is coating required: Anti-corrosion coatings such as nickel, zinc, epoxy resin (especially for humid or corrosive environments).
- Auxiliary materials: Support structure, yoke material (such as soft iron) or shielding requirements.
5. Mechanical and durability requirements
- Mechanical strength: Is it subject to vibration, impact or high-speed rotation? Consider the fixing method of the magnet (gluing, mechanical clamping, etc.).
- Life expectancy: Risk of demagnetization under long-term use (such as high temperature or reverse magnetic field).
- Maintainability: Is a removable or replaceable design required?
6. Production and cost constraints
- Quantity: Samples, small batches or mass production? Quantity directly affects the unit price.
- Delivery cycle: Is there an urgent delivery requirement?
- Budget range: Is there a cost optimization requirement for materials or processes (such as replacing NdFeB with ferrite)?
7. Testing and certification
- Test standards: Is a third-party magnetic field distribution test, temperature rise test, etc. required?
- Industry certification: Special certifications such as medical, aerospace or automotive industries (such as ISO 9001, RoHS, etc.).
8. Other special needs
- Customized services: Is simulation optimization required (such as finite element analysis to verify magnetic field design)?
- Logistics and packaging: Does the magnet require anti-magnetic packaging or special transportation conditions?
Why do we need these information?
The design of the Halbach array is highly dependent on the application scenario. For example, a high magnetic field density is required in the motor, while a uniform field distribution may be required for magnetic suspension.
Material selection affects performance and cost (such as NdFeB requires a high coercivity grade at high temperature).
The geometric dimensions and number of poles directly affect the spatial distribution of the magnetic field and the difficulty of manufacturing.
After providing the above details, the supplier can comprehensively evaluate the material, process and design complexity and give an accurate quotation and technical solution. If some parameters are uncertain, a professional magnet company can be commissioned to conduct simulation or prototype testing.